Form
The Form component in your application is a key interface element used for collecting and submitting data from users. It consists of various input fields (fieldset), buttons, and other interactive elements that allow users to provide information, which can then be processed or stored in the system. Forms are essential for user registration, login, surveys, data entry, and more.
Two types of forms type i.e. Legacy/Fill Form and Outline Form are given below:
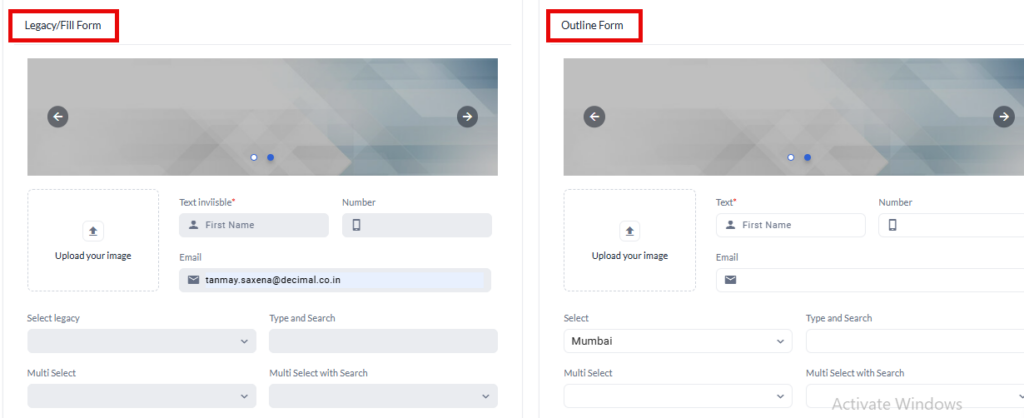
However, you can select between these formats while configuring the Fieldset Component.
Key Features:
- Input Fields:
The Form component supports various types of input fields, such as text boxes, dropdowns, checkboxes, radio buttons, and file upload options. These fields allow users to enter or select data. - Validation:
Built-in validation ensures that users provide the correct type of input in required fields. Common validations include email format, required fields, number ranges, and custom validation rules. - Submit and Reset Buttons:
The form typically includes a Submit button that triggers data submission and a Reset button that clears the form fields, allowing users to start over if needed. - Fieldset Support:
Forms can include Fieldset components to group related fields, making complex forms more organized and easier for users to navigate. - Error Messaging:
If validation fails or data is incorrect, the form displays error messages to guide users in correcting their input. These messages can appear next to the field or at the top of the form. - Data Binding:
The Form component can be connected to a data source or backend service, ensuring that submitted data is saved, processed, or validated through the system.
Common Use Cases:
- User Registration and Login:
Collect user credentials, such as email and password, for authentication purposes. - Surveys and Feedback:
Gather user responses through structured input fields to collect feedback or survey data. - Data Entry Forms:
Allow users to enter or update information, such as contact details, addresses, or product orders. - Payment and Checkout:
Forms are used for collecting payment information during the checkout process in e-commerce applications.
Creating a Form
- Under Inventory (
 ), click “Component“, which is on the second left panel.
), click “Component“, which is on the second left panel.
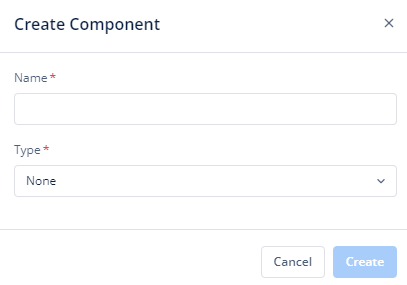
- Click Create placed on the second horizonal panel from the top, and a dialog box “Create Component” pops up.

- Select Type as “Form“, Name it in the text box and click “Create“.
- When you click Create (
 ), Basic option of Config menu for the Form opens.
), Basic option of Config menu for the Form opens. - Now you will see the following menu options:
- Basic
- Properties
- Style
- Animation
- Layout
- Events
- Elements
- Data
Note: You can create this component in the layout option of the configurator section as well. After this, you can follow the process given below.
Basic
| Basic Properties | Description |
| Type | The Component Type indicates the type of component you are adding. In this case, it defaults to “Form” and cannot be changed here. This selection is made initially when you create the component. |
| Reference Name | The Reference Name is a unique identifier assigned to the component for internal use. This name is visible only to vFlow users, and is not displayed to end-users. The Reference Name is intended for your convenience, helping you easily identify and manage the component throughout. |
| Description | The Description field is intended for use by application designers or administrators (vFlow users) to provide additional context or details about the component. This description is not visible to end-users and is used solely for internal reference to assist with component management. |
Properties
| Properties | Description |
| Tab Key Navigation | You can use the TAB key on the keyboard to move to the next field. |
| Expand Only One Fieldset | If some field sets are grouped in different accordions, the accordion being used will expand while others remain contracted. Note: Whether to group the fields into an accordion is defined under the Fieldset component configuration. |
| Header | It is displayed on the top of the component. To know more about header, click here or see the Header section under the System Components. |
| Footer | It is displayed on the bottom of the component. To know more about footer, click here or see the Footer section under the System Components. |
Style
The Style option allows you to personalize the appearance of the Form. This includes adjusting various visual aspects to ensure it complements your application’s branding and overall design. Here’s a breakdown of different settings that you can make adjustments to::
- Large Screen Width: The Form width is adjustable by entering a percentage value in the text box. For example, if the width is set to 100%, the Form will take the full width of the screen.
- Transparent: When you click to select this checkbox, the Form will have a transparent background, allowing it to blend into the background of the page or layout.
- Visible Scroll: To make the scroll visible, click to select the checkbox.
- Background Color: To choose the background color for the component, you can use a color picker or enter a hexadecimal or RGB color code. The default opacity is set to 100%.

- Font:
- Family: You can select the font family for text in the component. If no specific font is chosen, “None” will use the default font.
- Size: You can specify the font size in pixels (px).
- Color: You can set the font color using the color picker or a hexadecimal or RGB color code. The default opacity is 100%.

- Alphabet Case: You can choose the text case (e.g., uppercase, lowercase) or select “None” to keep the original case.
- Text Alignment: You can set the text alignment (e.g., left, center, right) or select “None” for default alignment.
- Dimension:
- Height: You can define the height of the component in pixels (px) or percentage (%).
- Maximum Height: You can set the maximum height to prevent the component from exceeding this limit.
- Width: You can specify the width of the component in pixels (px) or percentage (%).
- Maximum Width: You can define the maximum width to prevent the component from expanding beyond this size.
- Spacing:
- Margin: To adjust the space around the component, enter values for top, right, bottom, and left margins in pixels (px). Default is 0px for all sides.
- Padding: To set the internal space within the component, enter values for top, right, bottom, and left padding in pixels (px). Default is 0px for all sides.
- Border Radius: To define the curvature of the corners of the component, enter values for top-left, top-right, bottom-right, and bottom-left in pixels (px). Default is 0px for all corners.
- Custom CSS Class Name
- Users can enter custom CSS class names in the provided input field to apply additional styles.
- Multiple Classes Names can be provided, If needed. They can be applied by separating them with commas, as indicated by the example (
classA, classB).
These settings allow you to tailor Form to your specific design preferences and requirements.
Animation
This option allows you to apply several animations to enhance the component’s loading appeal. The following are the available animations:
- Bounce
- Flash
- Pulse
- Rubber Band
- Handshake
Their Configuration:
- Click the Type list, and then select an animation to apply an effect when the component loads.
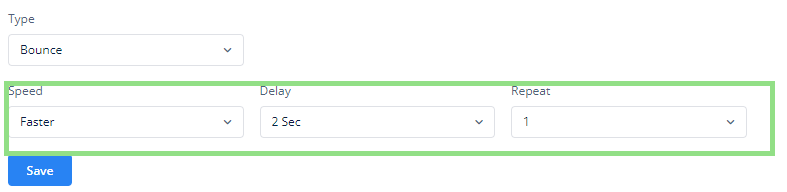
- After you select one of the animations (for example, Bounce), you will see the following configuration options:
- Speed: In this field, you can select one of the following options to adjust the speed of the animation:
- Faster
- Fast
- Slower
- Slow
- Delay: Click this list to select a value (for example, 3 seconds). This value specifies a time period. The application will load the animation after this time period (for example, 3 seconds).
- Repeat: In this list, select a value (for example, 2). This value specifies the total number of times the application will play the animation.
- Speed: In this field, you can select one of the following options to adjust the speed of the animation:
- After you configure the component’s animation properties, click
 to apply them to the component.
to apply them to the component.
Layout
You can learn more about configuring the layout in the Configurator section. However, it’s important to note a key difference when working with the Form component:
- This differs from the process in the Configurator, where you have the ability to create new components directly while configuring the form’s layout.
- When creating a Form component from the Inventory menu option in vFlow, you cannot create a new component directly from the Form’s layout option. Rather you have to make a new component separately and then map it to the form.
Note: In the Form layout, you can map only the Fieldset component.
Events
The Events option of the Form component, as shown in the image, allows you to assign task groups that will execute when specific actions occur within the component. These tasks can be created separately in the configurator or inventory and can be grouped to perform various actions when certain events are triggered.
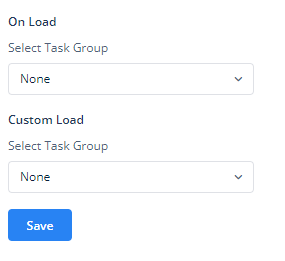
Here’s a breakdown of the Events section:
- On Load:
- This option lets you assign a task group that executes automatically when the component is loaded.
- You can select an existing task group from the dropdown list labeled Select Task Group or go back to the inventory or configurator to make a task or task group if needed.
- This could be useful for initializing data or triggering other actions as soon as the Form component is displayed.
- Custom Load:
- The Custom Load event enables you to trigger a specific task group during a customized loading scenario.
- Similar to the previous options, you can choose the task group to be executed from the Select Task Group dropdown list or go back to the inventory or configurator to make a task or task group if needed.
After assigning the appropriate task groups to these events, click the![]() button to apply your configuration to the component.
button to apply your configuration to the component.
In summary, the Events section provides flexibility in automating actions within your Form by linking predefined tasks to occur during the component’s loading process. This customization ensures a more dynamic and interactive user experience, tailored to your application’s specific needs.
Data
If you want to fetch and show some data in the card, select one of the data types that fits best for the business requirements:
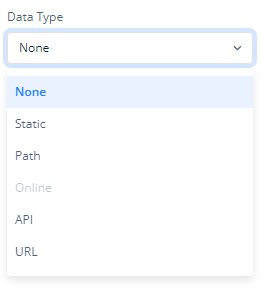
Note: To know more about Data, click here or check the post under configurator.
Reference
The Reference option becomes available when you open a Component, Task Group, or Business Rule from the page-level inventory that opens in the configurator, and the global inventory.
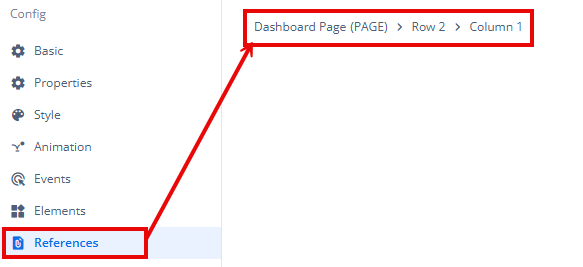
Since the global inventory contains all the Components, Task Groups, and Business Rules created in Vahana vFlow 2.0, it can be challenging to determine where these entities are mapped within the application. The Reference option provides a structured overview of all locations or items where a selected entity is mapped, offering a clear dependency view.
Example Mapping:
- Form > Row 1 > Column 1
This feature helps in efficiently tracking and managing dependencies across different sections of the application.
